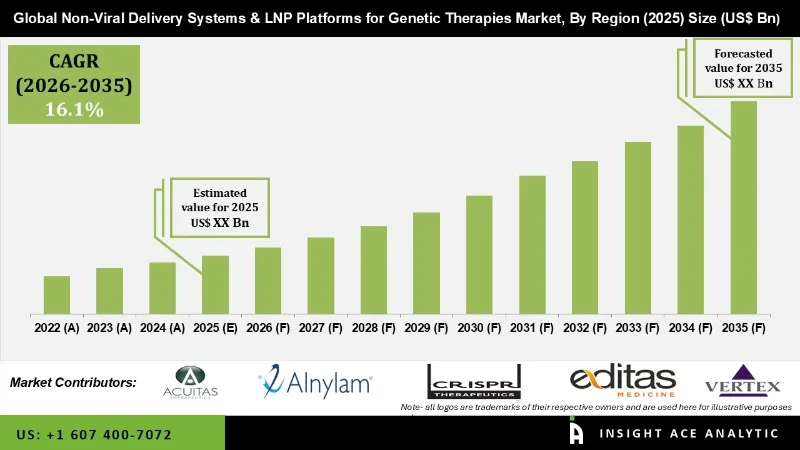
Non Viral Delivery Systems and LNP Platforms for Genetic Therapies Market is estimated to grow at a 16.1% CAGR during the forecast period for 2026 to 2035.
Non Viral Delivery Systems & LNP Platforms for Genetic Therapies Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis By Delivery Platform Type(Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs),Cell-Targeted LNPs (ctLNPs),Polymeric Nanoparticles, DNA-Based Nanocarriers), By Nucleic Acid Cargo(mRNA, siRNA, miRNA, Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs)), By Application Area(mRNA Therapeutics, RNA Interference (RNAi) Therapies, In Vivo Gene Editing, Gene Replacement Therapies, Protein Replacement via mRN), By Target Tissue / Organ(Liver, Lung (Inhaled / Nebulized Delivery), Immune Cells, Central Nervous System (CNS)), By Route of Administration(Intravenous (IV),Subcutaneous (SC),Intramuscular (IM), Inhalation / Pulmonary), By Stage of Development (Commercial / Approved Products, Phase III, Phase II), By End-User(Biopharmaceutical Companies, Gene Therapy Developers, RNA Therapeutics Companies, Academic & Research Institutes, Strategic Platform Partners Institutes Regulators) and Segment Forecasts, 2026 to 2035
Non-viral delivery systems are safe ways to send genetic material (DNA, RNA, or gene-editing tools) into human cells without using viruses. The most common and successful type is lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), tiny fat-based carriers that protect the genetic cargo, help it enter cells, and release it where it is needed. These systems are used to deliver mRNA medicines (like COVID-19 vaccines), RNA interference (RNAi) drugs, gene-editing tools (CRISPR), gene replacement, and protein replacement therapies. They are developed and used by biotech companies, research labs, and universities to turn new genetic treatments from experiments into real medicines for many diseases.
The growth of non-viral delivery systems and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) platforms for genetic therapies is being driven by several factors. There is a rising demand for gene and RNA-based treatments to address genetic disorders, cancers, and rare diseases. These technologies are becoming more popular because they are safer than viral methods and cause fewer immune reactions.
Advancements in LNPs and polymer-based carriers have made it easier to deliver genetic material efficiently to the right tissues or organs. The success of mRNA-based medicines such as COVID-19 vaccines, has further increased interest in these delivery systems. Additionally, more research and collaborations among biopharmaceutical companies, academic institutes, and other partners are helping to develop new and effective genetic therapies, making these technologies increasingly important in modern medicine.
The Global Non-Viral Delivery Systems & LNP Platforms for Genetic Therapies face several key challenges. Non-viral delivery methods often have lower transfection efficiency, means they may deliver genetic material less effectively than viral systems. They also face targeted delivery limitations, making it difficult to reach specific organs or cell types precisely. Molecular instability is another concern, as RNA and DNA can degrade quickly if not properly protected. Additionally, even these safe delivery systems can sometimes trigger unwanted immune responses, and the high costs of research and development make creating advanced delivery platforms expensive. Despite these challenges, ongoing innovation continues to improve the safety and effectiveness of these therapies. A major opportunity is the rapid growth of mRNA and RNA-based therapeutics, demonstrated by the success of COVID-19 vaccines. This success paves the way for personalized gene therapies, protein replacement treatments, and advanced genetic me
The main driver for the growth of non-viral delivery systems and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) platforms is the Use of LNP technology in mRNA-based therapies, which achieved major success during the COVID-19 pandemic. This real-world validation showed that non-viral delivery systems can safely and effectively deliver genetic material at a global scale. In contrast to viral vectors, these systems can be produced in large volumes, allow repeat dosing without major immune issues, and offer greater flexibility in treatment design. As a result, biopharmaceutical companies and researchers gained strong confidence in LNP platforms, leading to increased investment, wider adoption, and expanded development of gene and RNA-based therapies. This proves the evidence of safety, scalability, and effectiveness continues to be a key reason behind the strong growth of the market.
Achieving efficient delivery and precise targeting to specific extrahepatic tissues or cells is considered the biggest challenge for non-viral delivery systems and LNP platforms. While these technologies have proven highly effective in delivering genetic material to the liver, reaching other organs or specific cell types remains difficult. This is because the body’s natural barriers, circulation patterns, and cellular uptake mechanisms can prevent the therapy from reaching the intended site.
The inability to target tissues precisely can reduce treatment effectiveness, increase the risk of side effects, and limit the development of therapies for diseases beyond the liver, such as certain cancers, neurological disorders, or immune-related conditions. Addressing this challenge is therefore essential for expanding the clinical applications of non-viral delivery systems and completely realizing the potential of RNA- and DNA-based therapies.
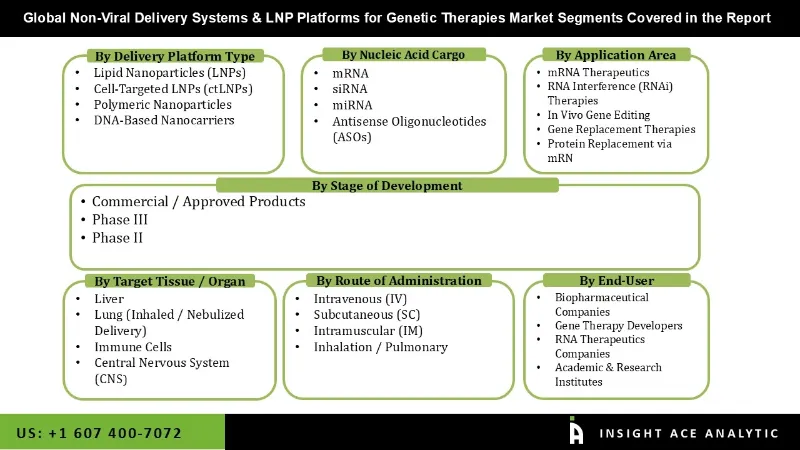
The Global Non-Viral Delivery Systems & LNP Platforms for Genetic Therapies Market is segmented across multiple dimensions, reflecting the rapid growth and technological diversity in non-viral gene delivery. By delivery platform type, it includes lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), cell-targeted LNPs (ctLNPs), polymeric nanoparticles, and DNA-based nanocarriers, each offering distinct advantages in stability, targeting, and delivery efficiency. Based on nucleic acid cargo, platforms support mRNA, siRNA, miRNA, and antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), enabling a wide range of therapeutic applications. By application area, the market encompasses mRNA therapeutics, RNA interference (RNAi) therapies, in vivo gene editing, gene replacement therapies, and protein replacement via mRNA, while target tissue segmentation focuses on the liver, lungs (inhaled or nebulized), immune cells, and the central nervous system (CNS). The market is further categorized by route of administration, including intravenous (IV), subcutaneous(SC)
Within the application area of non-viral delivery systems and LNP platforms, mRNA therapeutics and vaccines are the leading segment. These therapies work by delivering mRNA molecules into cells, which instruct the cells to produce specific proteins that can either treat diseases, replace missing proteins, or stimulate the immune system. The success of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines demonstrated the potential of this approach on a global scale, proving that mRNA-based treatments can be safe, effective, and manufactured rapidly at large volumes. Beyond vaccines, mRNA therapeutics are being developed for a range of applications, including cancer immunotherapy, rare genetic disorders, protein replacement therapies, and infectious diseases. The versatility of mRNA, combined with advances in lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery technology, allows precise targeting, improved stability, and reduced immune reactions, making it a cornerstone of next-generation genetic medicine. This strong performance has led to increased invest
Within non-viral delivery systems and LNP platforms, intravenous (IV) administration is the most widely used route for delivering genetic material. This method allows therapies to be directly introduced into the bloodstream, ensuring rapid and efficient distribution to target tissues, especially the liver and other highly vascularized organs. IV administration is particularly effective for mRNA therapeutics, RNA interference (RNAi) therapies, and gene replacement treatments, as it maximizes delivery efficiency while maintaining safety. Its reliability, precision, and scalability make it the preferred choice for both clinical trials and approved therapies, supporting the broader adoption of non-viral genetic therapies worldwide.
North America dominates the global non-viral delivery systems and LNP platforms market due to a combination of advanced biotechnology infrastructure, strong government and private funding, and a culture of rapid adoption of innovative therapies. The region is home to pioneering companies and research institutes that are at the forefront of developing RNA-based therapies, gene editing, and protein replacement treatments. The early success and widespread implementation of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in North America validated LNP technology on a massive scale, boosting confidence in non-viral delivery methods. Additionally, high patient awareness, well-established clinical trial networks, and favorable regulatory pathways make it easier to test, approve, and commercialize new therapies quickly. The presence of strategic collaborations between industry and research institutions also accelerates innovation, giving North America a clear edge in the development and adoption of cutting-edge genetic therapies.
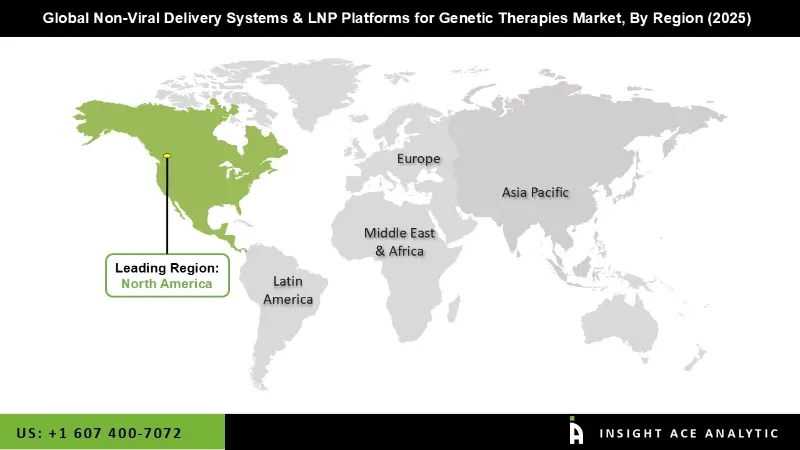
The Asia-Pacific region is rapidly growing due to the fast expansion of biotechnology infrastructure, increasing investments in genetic therapies, and rising healthcare awareness. Countries like China, Japan, and India are seeing rising adoption of RNA-based therapies and participation in clinical trials, driving strong market growth in the region.
• November 2025: Acuitas Therapeutics had announced its next-generation Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) technology, highlighting advancements in potency, safety, and extra-hepatic (beyond the liver) delivery. This technology was notably used in the world's first personalized CRISPR therapy administered to an infant with a rare genetic disease.
| Report Attribute | Specifications |
| Growth Rate CAGR | CAGR of 16.1% from 2026 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | Representation of revenue in US$ Bn and CAGR from 2026 to 2035 |
| Historic Year | 2022 to 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 to 2035 |
| Report Coverage | The forecast of revenue, the position of the company, the competitive market structure, growth prospects, and trends |
| Segments Covered | By Delivery Platform Type, Nucleic Acid Cargo, Application Area, Target Tissue, Route of Administration, Stage of Development, End-User. |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
| Country Scope | U.S.; Canada; U.K.; Germany; China; India; Japan; Brazil; Mexico; The UK; France; Italy; Spain; China; Japan; India; South Korea; Southeast Asia; South Korea; Southeast Asia |
| Competitive Landscape | Acuitas Therapeutics, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Arcturus Therapeutics, Beam Therapeutics, Code Biotherapeutics, CRISPR Therapeutics, CureAge Therapeutics, Editas Medicine, Evox Therapeutics, GenEdit, Genevant Sciences, Generation Bio, Genprex, Intellia Therapeutics, Moderna, NanoVation Therapeutics, Orna Therapeutics, ReCode Therapeutics, STRM.BIO, Vertex Pharmaceuticals. |
| Customization Scope | Free customization report with the procurement of the report, Modifications to the regional and segment scope. Geographic competitive landscape. |
| Pricing and Available Payment Methods | Explore pricing alternatives that are customized to your particular study requirements. |
North America-
Europe-
Asia-Pacific-
Latin America-
Middle East & Africa-
This study employed a multi-step, mixed-method research approach that integrates:
This approach ensures a balanced and validated understanding of both macro- and micro-level market factors influencing the market.
Secondary research for this study involved the collection, review, and analysis of publicly available and paid data sources to build the initial fact base, understand historical market behaviour, identify data gaps, and refine the hypotheses for primary research.
Secondary data for the market study was gathered from multiple credible sources, including:
These sources were used to compile historical data, market volumes/prices, industry trends, technological developments, and competitive insights.
Primary research was conducted to validate secondary data, understand real-time market dynamics, capture price points and adoption trends, and verify the assumptions used in the market modelling.
Primary interviews for this study involved:
Interviews were conducted via:
Primary insights were incorporated into demand modelling, pricing analysis, technology evaluation, and market share estimation.
All collected data were processed and normalized to ensure consistency and comparability across regions and time frames.
The data validation process included:
This ensured that the dataset used for modelling was clean, robust, and reliable.
The bottom-up approach involved aggregating segment-level data, such as:
This method was primarily used when detailed micro-level market data were available.
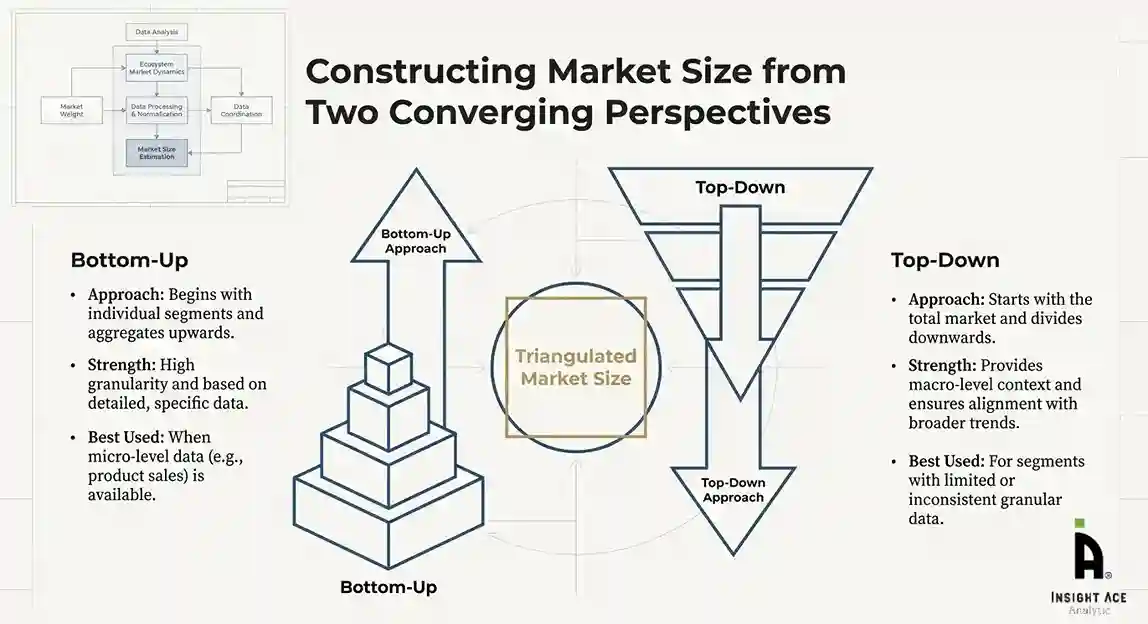
The top-down approach used macro-level indicators:
This approach was used for segments where granular data were limited or inconsistent.
To ensure accuracy, a triangulated hybrid model was used. This included:
This multi-angle validation yielded the final market size.
Market forecasts were developed using a combination of time-series modelling, adoption curve analysis, and driver-based forecasting tools.
Given inherent uncertainties, three scenarios were constructed:
Sensitivity testing was conducted on key variables, including pricing, demand elasticity, and regional adoption.