Immune Cell Engagers (ICEs) Market is expected to grow with at a 26.4% CAGR during the forecast period for 2026 to 2035.
Immune Cell Engagers (ICEs) Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Distribution by Product Type (Bispecific Antibodies, Trispecific/Multispecific Antibodies, Engineered Cell Therapies), By Target Antigen (Oncology Targets, Autoimmune/Inflammatory Targets), By Mechanism of Action (Immune Cell Recruitment, Signal Modulation, Conditional Activation), By Therapeutic Area (Oncology, Autoimmune/Inflammatory), Development Stage (Clinical Phase, Marketed/Approved) and Segment Forecasts, 2026 to 2035
-Market-info.webp)
Immune cell engagers (ICEs) are specially designed antibody medicines that connect the body’s immune cells (mainly T cells and NK cells) directly to cancer cells. They work by binding to one spot on the immune cell and another spot on the cancer cell, bringing them close together so the immune cell can attack and destroy the cancer. Unlike CAR-T therapy, ICEs are ready-to-use “off-the-shelf” drugs—no need to modify the patient’s own cells. They have shown very good results in blood cancers like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, and researchers are now testing them for solid tumors and some autoimmune diseases.
The two main categories of ICEs include T-cell engager proteins (TCEs), commonly known as Bi-specific T-cell engager proteins (BiTEs), NK-cell engagers (NKCEs), and macrophageCannabinoid inhalational products consisted of electronic vaporizers, metered-dose inhalers, dry powder inhalers, and nebulized formulations. These had wide applications for pain relief, auxiliary, epileptic, nausea, and lung and central nervous system disorders, mainly for their rapid functional relief.
Rapid growth in medical cannabis legalization, increasing acceptance for non-smoking cannabis dosing, as well as technological advancements for inhalational systems, represented major driving forces for this market. Nevertheless, lack of regulatory clarity, safety issues with chronic inhalational exposure, as well as differing quality standards pertaining to these regions, still represented some prime restraints for this market.
Medical & Pharmaceutical-Grade Inhalation Companies
The key driving factor for the Immune Cell Engagers (ICEs) market is their effectiveness in treating refractory and relapsed cancer while overcoming the complexity associated with cell therapies. ICEs can utilise a patient's immune system to target and destroy cancerous cells, using T and NK cells, hence not requiring manipulating any cells ex vivo, unlike in CAR T-cell therapies. This makes them more scalable and potentially more affordable and quicker to develop, hence quicker to be adopted by the medical and biotechnology business sectors. On the other hand, successful medical outcomes in haematological cancers, together with improvements in antibody engineering, including half-life and multivalent designs, are broadening their treatment use.
The biggest concern for Immune Cell Engagers (ICEs) is related to immune activation and its effects on safety and tolerability. ICEs may cause adverse reactions including cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurotoxicity, and on-target off-tumor toxicity, especially if target antigens are present in normal tissues. This makes dose optimization more difficult, narrows the therapeutic window, and may delay development and clearance by regulatory agencies, particularly in solid tumors for which immune control may be more challenging.
Bispecific antibodies are anticipated to propel the Immune Cell Engagers (ICEs) market because of increased validation, scalability, and commercial maturity. Various bispecific T-cell engagers are presently showing excellent efficacy in hematologic cancers and are approved and in late-stage pipelines, immediately translating into near-term financial growth. Although trispecific/multispecific and engineered cell therapies display excellent future growth potential, they face significant complexity and toxicity issues and are currently in earlier stages of development, whereas bispecific antibodies display more familiarity with regulatory agencies and relative ease in development, thus representing the prime drivers for the market at present. Bispecific antibodies and engineered cell therapies display significant potential for future growth but are in earlier stages of development due to increased complexity and toxicity issues.
The oncology targets segment is growing at the fastest rate. Notably, this is due to the high growth rate of Immune Cell Engagers in cancer treatment, including hematologic malignancies and, recently, in solid tumours. Their high clinical effectiveness in resistant cancers, a promising development pipeline of ICEs targeting antigens associated with tumours (such as CD19, BCMA, and HER2), and investments by the biopharma industry are driving advancements. In contrast, their uses in autoinflammatory and autoimmune indications are relatively earlier-stage and less numerous, categorizing cancer indications as the fastest-growing market in the ICEs market.
North America is the most dominant region in the Immune Cell Engagers (ICEs) market. This dominance is primarily aided by the strong biopharmaceutical infrastructure, high density of clinical trials and key players in the field of oncology medications, rapid regulatory approvals, and intense investments in immuno-oncology research and development in the region. Additionally, the region enjoys sophisticated healthcare infrastructure and quick uptake of innovative biologics and the key players are actively pursuing the development of bispecific and multispecific antibodies in the ICEs market.
-Market-region.webp)
March 2025: Sanofi and Dren Bio, Inc. entered into a definitive agreement under which Sanofi agreed to acquire DR-0201, a targeted bispecific myeloid cell engager (MCE) that had demonstrated robust B-cell depletion in preclinical and early clinical studies.
| Report Attribute | Specifications |
| Growth Rate CAGR | CAGR of 26.4% from 2026 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | Representation of revenue in US$ Bn and CAGR from 2026 to 2035 |
| Historic Year | 2022 to 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 to 2035 |
| Report Coverage | The forecast of revenue, the position of the company, the competitive market structure, growth prospects, and trends |
| Segments Covered | Product Type, Target Antigen, Mechanism of Action, Therapeutic Area, Development Stage |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
| Country Scope | U.S.; Canada; U.K.; Germany; China; India; Japan; Brazil; Mexico; The UK; France; Italy; Spain; China; Japan; India; South Korea; Southeast Asia; South Korea; Southeast Asia |
| Competitive Landscape | Amgen (Blinatumomab), Johnson & Johnson/Genmab (Teclistamab), Regeneron (Odronextamab), Pfizer (Elranatamab), Sanofi (SAR446309), Affimed (AFM13), Innate Pharma (IPH6101), Dragonfly Therapeutics (DF1001), GT Biopharma (GTB-3550), Immunocore (Tebentafusp), Merus (MCLA-158), Xencor (Plamotamab), Harpoon Therapeutics (HPN328), Gilead/Tizona (TTX-080), Jounce Therapeutics (JTX-8064), UCB Pharma (CD19×CD3), Horizon Therapeutics/Amgen (B-cell depleters), Viela Bio (CD40L×CD3), MorphoSys (CD19×CD3), CytomX (Probody TCE), Xilio Therapeutics (Tumor-activated), Numab Therapeutics (NM21-1480), Immatics (IMA401) |
| Customization Scope | Free customization report with the procurement of the report, Modifications to the regional and segment scope. Geographic competitive landscape. |
| Pricing and Available Payment Methods | Explore pricing alternatives that are customized to your particular study requirements. |
-Market-seg.webp)
North America-
Europe-
Asia-Pacific-
Latin America-
Middle East & Africa-
This study employed a multi-step, mixed-method research approach that integrates:
This approach ensures a balanced and validated understanding of both macro- and micro-level market factors influencing the market.
Secondary research for this study involved the collection, review, and analysis of publicly available and paid data sources to build the initial fact base, understand historical market behaviour, identify data gaps, and refine the hypotheses for primary research.
Secondary data for the market study was gathered from multiple credible sources, including:
These sources were used to compile historical data, market volumes/prices, industry trends, technological developments, and competitive insights.
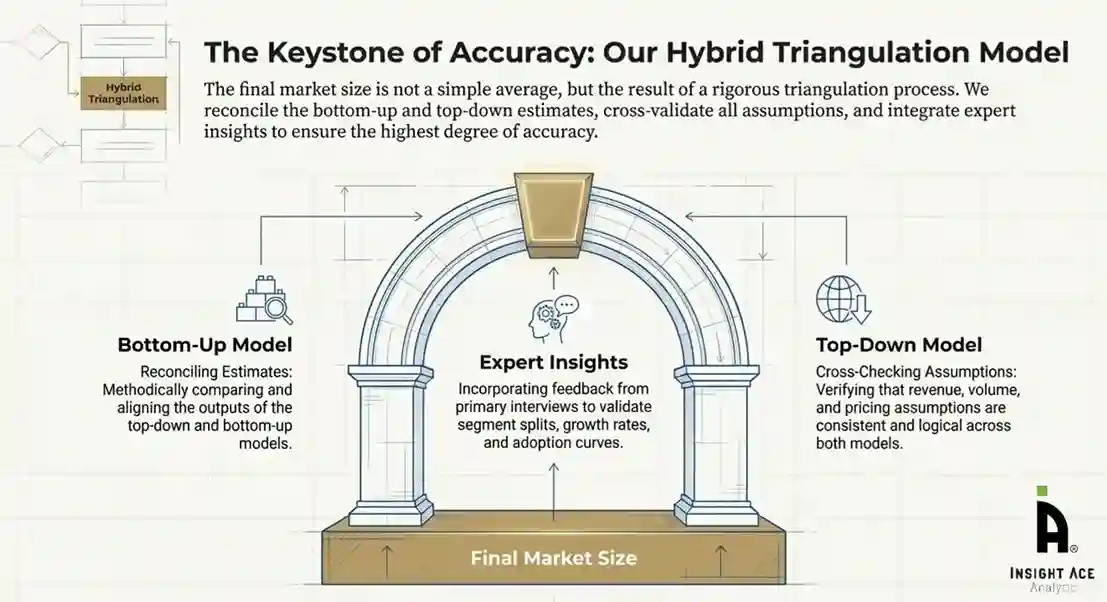
Primary research was conducted to validate secondary data, understand real-time market dynamics, capture price points and adoption trends, and verify the assumptions used in the market modelling.
Primary interviews for this study involved:
Interviews were conducted via:
Primary insights were incorporated into demand modelling, pricing analysis, technology evaluation, and market share estimation.
All collected data were processed and normalized to ensure consistency and comparability across regions and time frames.
The data validation process included:
This ensured that the dataset used for modelling was clean, robust, and reliable.
The bottom-up approach involved aggregating segment-level data, such as:
This method was primarily used when detailed micro-level market data were available.
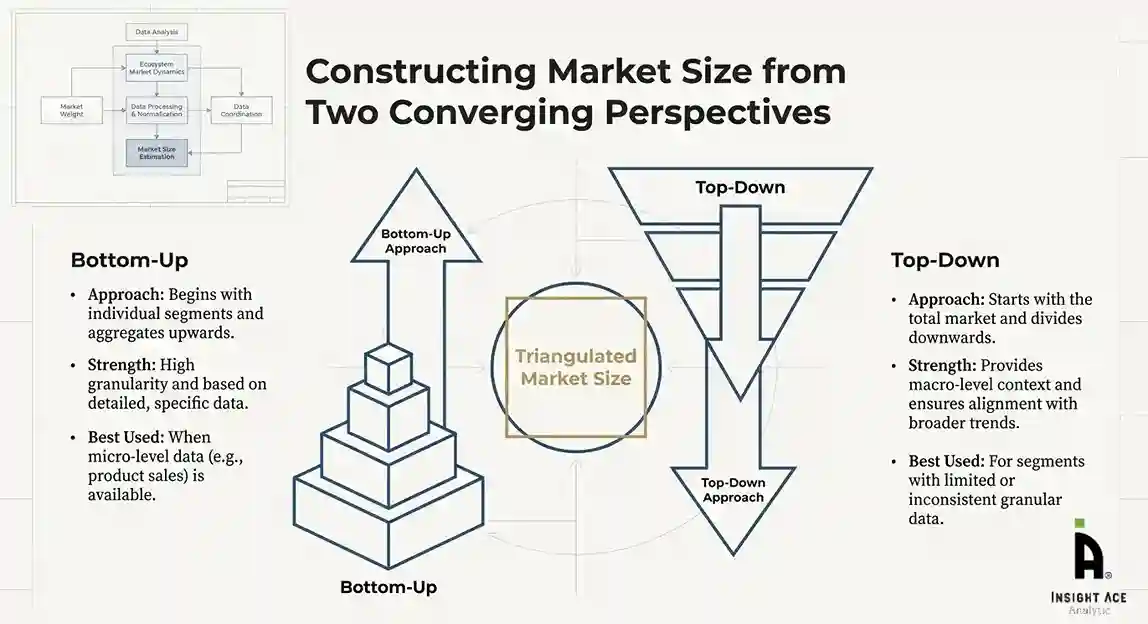
The top-down approach used macro-level indicators:
This approach was used for segments where granular data were limited or inconsistent.
To ensure accuracy, a triangulated hybrid model was used. This included:
This multi-angle validation yielded the final market size.
Market forecasts were developed using a combination of time-series modelling, adoption curve analysis, and driver-based forecasting tools.
Given inherent uncertainties, three scenarios were constructed:
Sensitivity testing was conducted on key variables, including pricing, demand elasticity, and regional adoption.