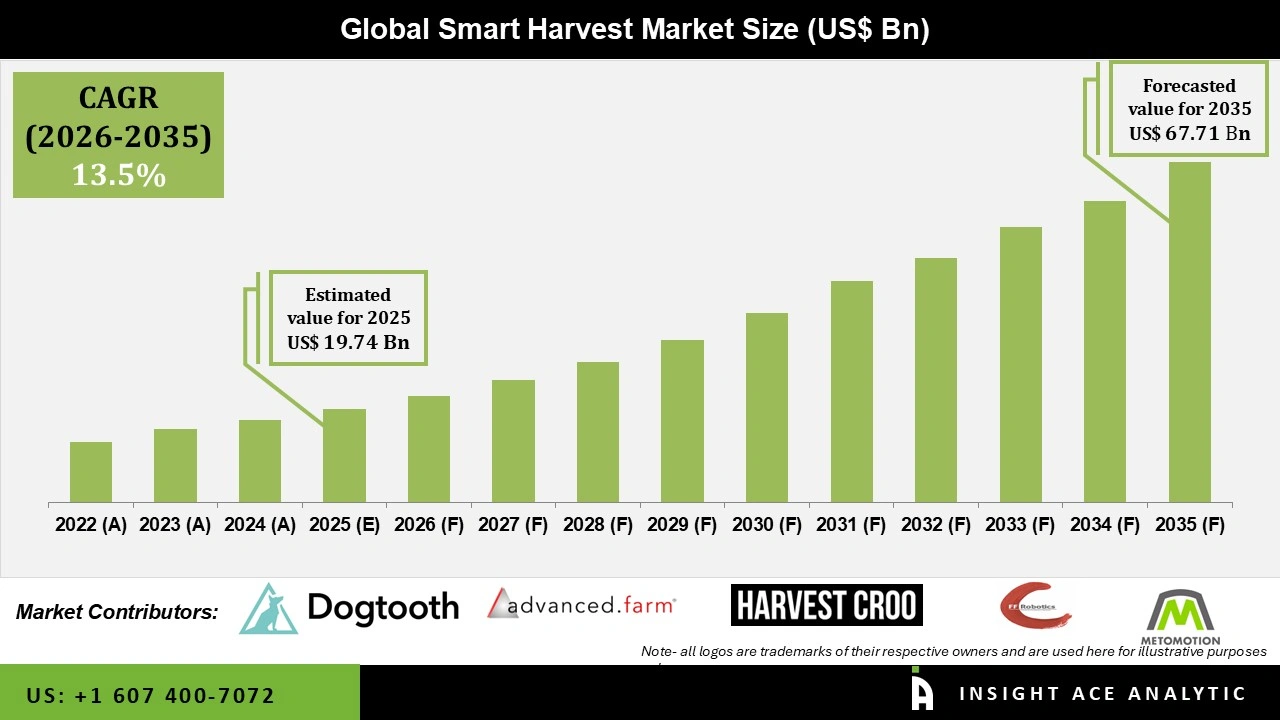
Global Smart Harvest Market Size is valued at USD 19.74 Bn in 2025 and is predicted to reach USD 67.71 Bn by the year 2035 at a 13.5% CAGR during the forecast period for 2026 to 2035.
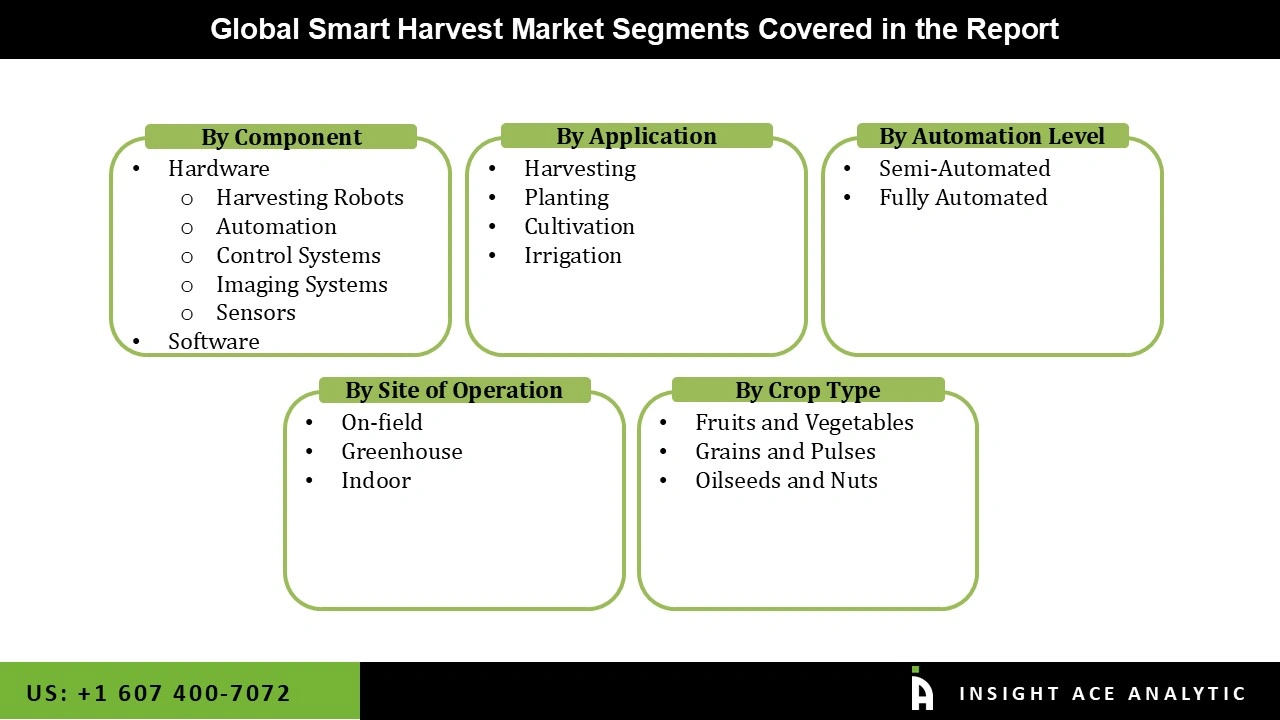
Smart Harvest Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Distribution by Component (Software and Hardware (Harvesting Robots, Control Systems, Automation, Sensors, Imaging Systems)), Operation Site (On-field, Indoor, and Greenhouse), Automation Level (Semi-Automated and Fully Automated), Application (Harvesting, Cultivation, Planting, and Irrigation), Crop Type (Grains and Pulses, Fruits and Vegetables, Oilseeds and Nuts),By Region and Segment Forecasts, 2026 to 2035.
Smart harvest, also referred to as precision agriculture harvesting or intelligent harvesting, denotes the application of advanced technological systems and data-driven approaches to optimise the harvesting phase within modern agricultural production. This paradigm integrates a suite of innovations including satellite-based global positioning systems (GPS), automated and robotic harvesters, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, unmanned aerial vehicles (drones), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning algorithms, and real-time data analytics to achieve greater precision, efficiency, and sustainability during crop collection.
The primary objectives are to determine optimal harvest timing for maximum yield and quality, minimise mechanical damage to crops, reduce labour intensity and physical workload on workers, decrease resource consumption (fuel, water, and inputs), and enhance adaptability to environmental variability such as fluctuating weather patterns and soil heterogeneity. By addressing persistent challenges in traditional agriculture including labour shortages, rising global food demand, climate-induced uncertainties, and sustainability imperatives—smart harvest technologies enable consistent production of high-quality crops with reduced operational strain, thereby supporting the transition toward resilient, resource-efficient, and economically viable farming systems. The rapid evolution of the smart harvest sector is propelled by the pressing need to simultaneously increase agricultural productivity and decrease production costs in response to demographic and environmental pressures.
The integration of smart technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics is growing in popularity as farmers and agricultural enterprises want to increase production and efficiency. This change tackles the problems caused by labour shortages and environmental concerns, in addition to optimising resource use. However, the smart harvest market confronts various challenges like the high price of cutting-edge technology and its sluggish uptake in poorer nations. Despite these obstacles, growth is being propelled by substantial investments in research and technology as well as government backing for sustainable agriculture. Furthermore, improving accessibility and fostering the smart harvest market expansion are the results of the development of scalable harvesting systems for smaller farms.
Driver
Increasing Government Assistance to Advance Smart Farming
The growing government support seen worldwide to encourage the adoption of technologies that support smart farming is expected to fuel the growth of the global smart harvest market. Many nations view agriculture as their foundation. The demand and consumption of food items have increased exponentially due to the growing population. In the forecastiing years, this trend is anticipated to drive market growth. But the growing need for food throughout the world may be too much for conventional farming methods, which is driving the creation and uptake of innovative technologies that lessen manual labor and help increase crop yield while preserving the quality of the finished products. Because of this, regional governments are now encouraging the use of smart systems.
Restrain/Challenge
Growing Technical Complexities
One major barrier to the growth of the global smart harvest market is the technical complexity needed to imitate human dexterity in robotic gripping systems. Although bulk crops can be handled efficiently by mechanized systems, market penetration in the fresh produce industry is significantly limited by existing technology's incapacity to handle soft produce, such as tomatoes, berries, and stone fruits, gently without causing damage. For high-value crops, this technical disparity pushes farmers to continue using manual labour, offsetting the potential cost savings and operational efficiency that motivate automation investments. In contrast to other areas of agricultural automation, harvest-specific robotics adoption rates have stagnated. Moreover, more training expenditures are necessary since many farmers lack the technical know-how to efficiently operate sophisticated harvesting technologies.
The indoor category held the largest share in the Smart Harvest market in 2025. It is anticipated that the lack of fertile land in emerging nations would accelerate indoor farming's income development and lead to a further expansion in the use of robots and smart harvest technology. Additionally, the use of indoor farming techniques is being driven by growing labour costs as a result of a loss in the agricultural workforce, particularly in many wealthy nations. The use of conventional harvesting equipment and related labour costs is eliminated by indoor farming and automated harvesting equipment. Furthermore, indoor farming, which mostly consists of container and vertical farming, necessitates a controlled atmosphere. By assisting growers in determining when crops are ready for harvest, IoT sensors and high-resolution multispectral cameras in indoor farming greatly minimize crop waste.
In 2025, the Grains and Pulses category dominated the Smart Harvest market, as farmers use precise harvesting techniques to increase yields, lower losses after harvest, and satisfy the growing demand for food security. Cereal and legume farmers can now optimize combine settings, moisture management, and real-time logistics with sensors, machine-guidance systems, and data-driven harvest scheduling. These advancements are particularly beneficial for bulk, commodity crops where even small efficiency gains can have a significant economic impact. More automation in emerging economies, more reasonably priced IoT devices and mobile connectivity in rural areas, and more investment from agritech companies that offer integrated hardware-software harvest solutions are further factors driving the smart harvest market expansion.
The North American region held the largest share of the Smart Harvest market due to the increased use of advanced technologies by farmers across the region. North America has vast agricultural land, and its farmers are not only financially stable but also technically skilled enough to implement modern farming practices that improve the quality of their produce. Both regional farmers and large agricultural enterprises have adopted contemporary techniques to reduce crop waste and prevent degradation caused by changing environmental conditions, thereby creating greater opportunities for smart harvesting solutions.
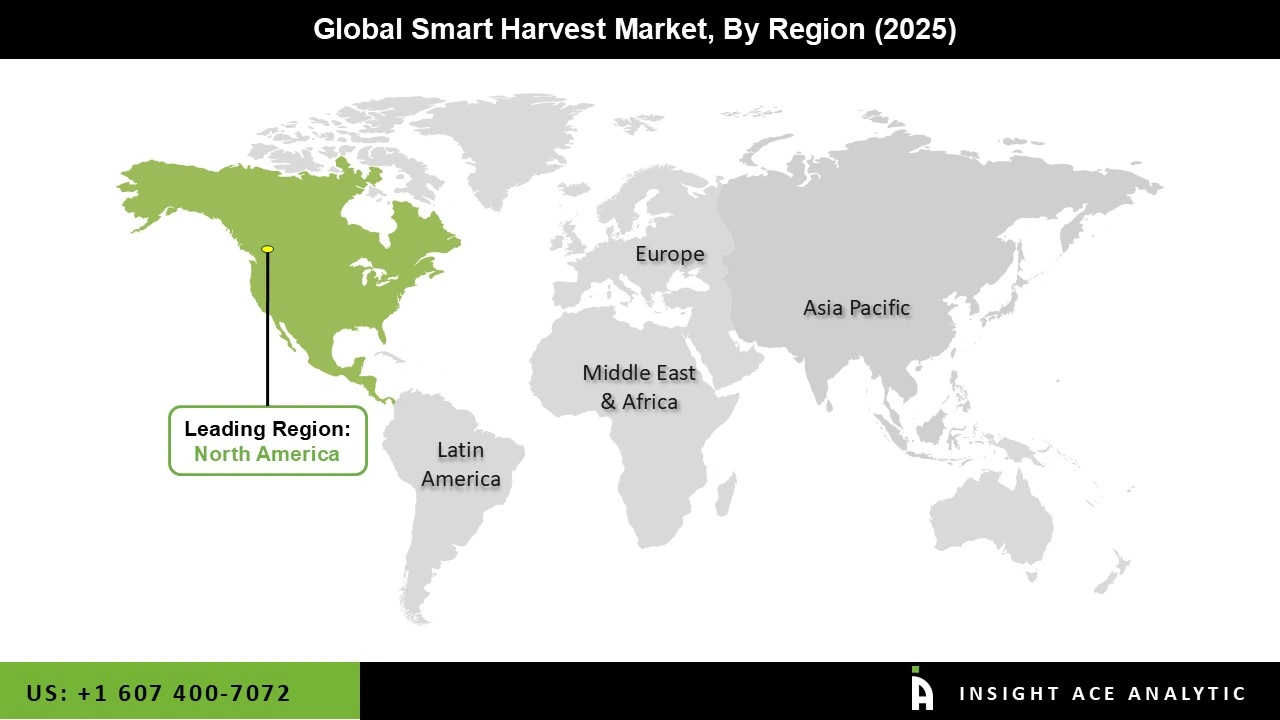
Additionally, strong support from governments in the region has significantly contributed to market expansion, with substantial focus placed on modernizing and strengthening the agricultural sector. Furthermore, several major technology companies in North America are specifically developing innovative solutions for the agricultural industry, further accelerating market growth.
March 2025: Trimble unveiled IonoGuard, an RTK GNSS system that minimises interference in precision farming operations by maintaining precise signal tracking during solar storms. The method increases the dependability of autonomous and intelligent harvesting systems by guaranteeing constant satellite guidance.
| Report Attribute | Specifications |
| Market size value in 2025 | USD 19.74 Bn |
| Revenue forecast in 2035 | USD 67.71 Bn |
| Growth Rate CAGR | CAGR of 13.5% from 2026 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | Representation of revenue in US$ Bn and CAGR from 2026 to 2035 |
| Historic Year | 2022 to 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026-2035 |
| Report Coverage | The forecast of revenue, the position of the company, the competitive market structure, growth prospects, and trends |
| Segments Covered | Component, Operation Site, Automation Level, Application, Crop Type, and By Region |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
| Country Scope | U.S.; Canada; U.K.; Germany; China; India; Japan; Brazil; Mexico; France; Italy; Spain; South Korea; Southeast Asia |
| Competitive Landscape | John Deere, Agrobot, Harvest CROO Robotics LLC, Octinion, Tortuga Agriculture Technologies Inc, Organifarms GmbH, Agrist Inc., Dogtooth Technologies Limited, FFRobotics, CNH Industrial America LLC, Mycionics Inc, Trimble Inc., Advanced Farms Technologies Inc, MetoMotion, and SoftGripping GmbH |
| Customization Scope | Free customization report with the procurement of the report, Modifications to the regional and segment scope. Geographic competitive landscape. |
| Pricing and Available Payment Methods | Explore pricing alternatives that are customized to your particular study requirements. |
This study employed a multi-step, mixed-method research approach that integrates:
This approach ensures a balanced and validated understanding of both macro- and micro-level market factors influencing the market.
Secondary research for this study involved the collection, review, and analysis of publicly available and paid data sources to build the initial fact base, understand historical market behaviour, identify data gaps, and refine the hypotheses for primary research.
Secondary data for the market study was gathered from multiple credible sources, including:
These sources were used to compile historical data, market volumes/prices, industry trends, technological developments, and competitive insights.
Primary research was conducted to validate secondary data, understand real-time market dynamics, capture price points and adoption trends, and verify the assumptions used in the market modelling.
Primary interviews for this study involved:
Interviews were conducted via:
Primary insights were incorporated into demand modelling, pricing analysis, technology evaluation, and market share estimation.
All collected data were processed and normalized to ensure consistency and comparability across regions and time frames.
The data validation process included:
This ensured that the dataset used for modelling was clean, robust, and reliable.
The bottom-up approach involved aggregating segment-level data, such as:
This method was primarily used when detailed micro-level market data were available.
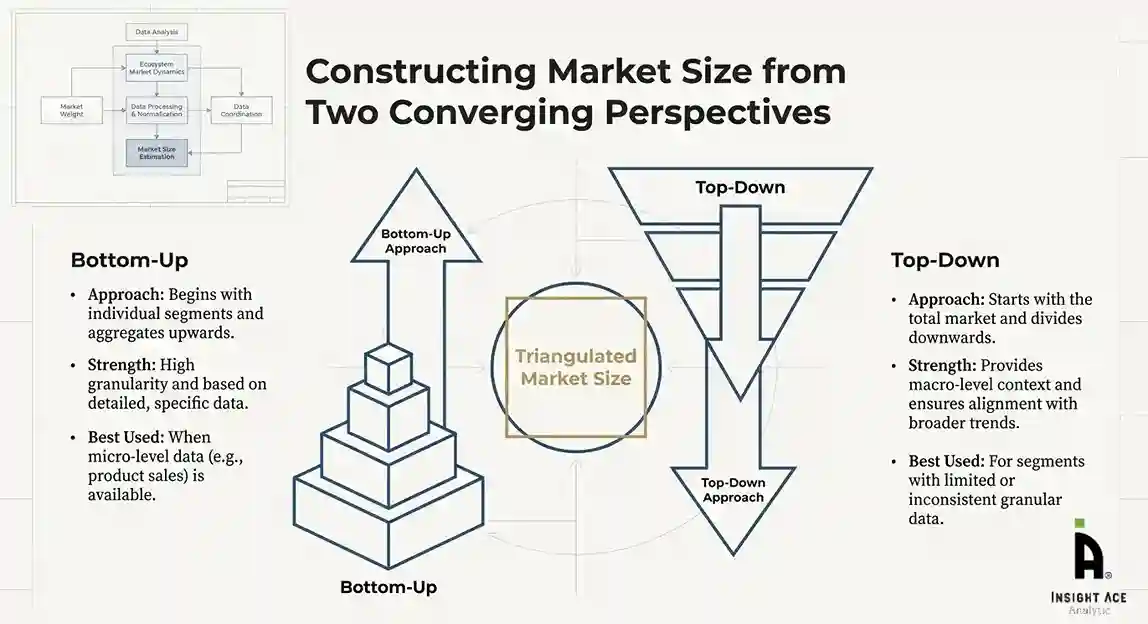
The top-down approach used macro-level indicators:
This approach was used for segments where granular data were limited or inconsistent.
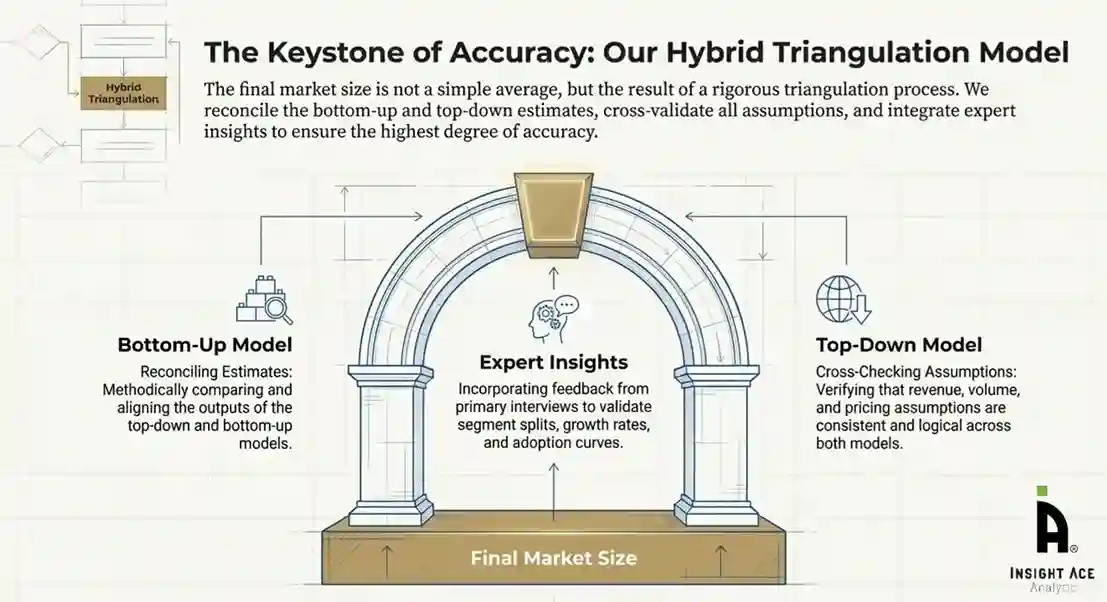
To ensure accuracy, a triangulated hybrid model was used. This included:
This multi-angle validation yielded the final market size.
Market forecasts were developed using a combination of time-series modelling, adoption curve analysis, and driver-based forecasting tools.
Given inherent uncertainties, three scenarios were constructed:
Sensitivity testing was conducted on key variables, including pricing, demand elasticity, and regional adoption.