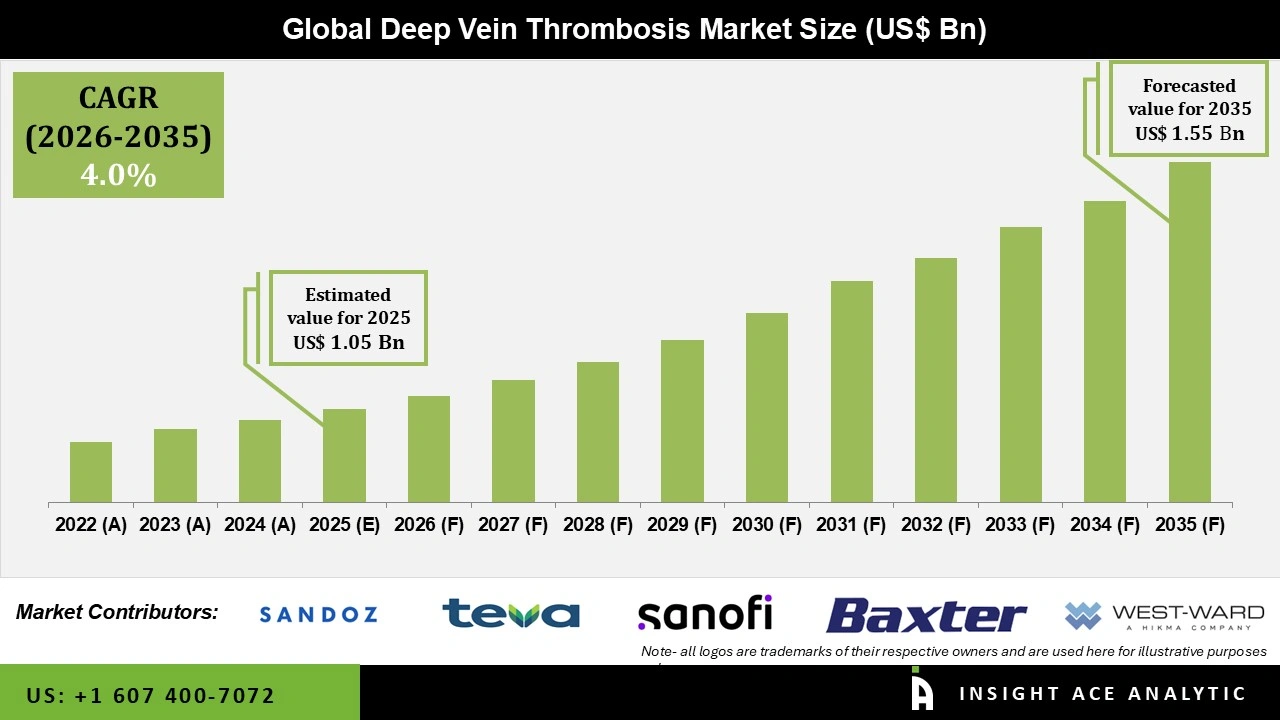
Global Deep Vein Thrombosis Market Size is valued at USD 1.05 Billion in 2025 and is predicted to reach USD 1.55 Billion by the year 2035 at a 4.0 % CAGR during the forecast period for 2026 to 2035.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Treatment (Clot Busters, Blood Thinners, Inferior Vena Cava Filters, Compression Stockings, Others), By Distribution Channel, Region And Segment Forecasts, 2026 to 2035.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that occurs when clots forms in the deep veins of the body. The most dangerous complication of deep vein thrombosis is pulmonary embolism (PE), which can either be asymptomatic or symptomatic. Surgery and pregnancy are the major risk factors associated with deep vein thrombosis. Pregnancy increase hormone level and slower blood flow lead to expansion of uterus and restrict blood flowing back from lower extremities responsible for deep vein thrombosis. Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis can be made with blood tests such as D-dimer test and imaging tests such as Doppler ultrasound (Duplex), contrast venogram, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computer tomography (CT). There are four types of treatments for deep vein thrombosis include anticoagulant, thrombolytic therapy, IVC filters (Vein Filters), and Stents. Anticoagulant such as unfractionated heparin, low molecular weight heparin (enoxaparin/ Lovenox, dalteparin/Fragmin, or tinzaparin/Innohep, fondaparinux/Arixtra or desirudin/Iprivask), warfarin (Coumadin and Jantoven) are the primary treatment deep vein thrombosis. Thrombolytic therapy such as tissue plasminogen activator agents (tPA) can help to dissolve the blood clot. IVC filters (Vein Filters), also known as “Greenfield filters,” is an umbrella-shaped device that is placed into the large vein, which traps blood clots and prevents deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Stents are metal meshwork tubes that are placed into a vein to keep them open.
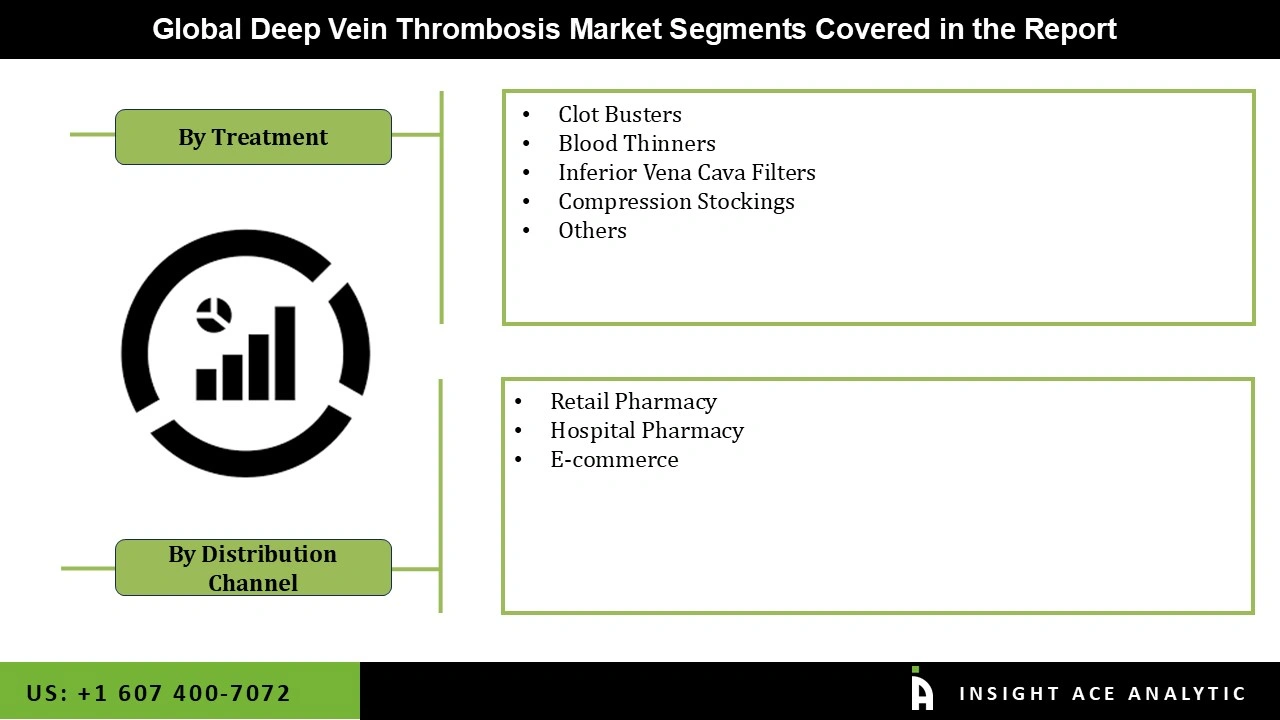
Deep Vein Thrombosis market is segmented into Treatement, Distribution channel and Region. On the basis of Treatment, market is segmented into Clot Busters, Blood Thinners, Inferior Vena Cava Filters, Compression Stockings, Others, on the other side, By Distribution Channel, market is devided into Retail Pharmacy, Hospital Pharmacy, and E-commerce. Regionally, market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa.
Almost one-half million patients are hospitalized for venous thromboembolism (consist of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) each year in the United States. In Europe, there are 544,000 venous thromboembolism related death every year. Venous thromboembolism can cause a significant global economic burden. Various diagnostic tests and treatment, prolonged hospital stay, and follow-up care can be extremely costly; for instance estimated medical cost for venous thromboembolism in the U.S is $5-10 billion per year. In U.K venous thromboembolism related cost is 750 million per year. In Australia, venous thromboembolism related costs are estimated at 1.72 billion a year. In June 2017, U.S. FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approved betrixaban (Portola) for the adult with venous thromboembolism (VTE). Pentasaccharides such XARELTO are novel anticoagulants may be preferred over standard therapy due to few drug interactions and no need for frequent monitoring or re-dosing.
| Report Attribute | Specifications |
| Market Size Value In 2025 | USD 1.05 Billion |
| Revenue Forecast In 2035 | USD 1.55 Billion |
| Growth Rate CAGR | CAGR of 4.0% from 2026 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | Representation of revenue in US$ Million and CAGR from 2026 to 2035 |
| Historic Year | 2022 to 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026-2035 |
| Report Coverage | The forecast of revenue, the position of the company, the competitive market structure, growth prospects, and trends |
| Segments Covered | By Treatment, By Distribution Channel |
| Regional Scope | North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
| Country Scope | U.S.; Canada; U.K.; Germany; China; India; Japan; Brazil; Mexico; The UK; France; Italy; Spain; China; Japan; India; South Korea; South East Asia; South Korea; South East Asia |
| Competitive Landscape | Sandoz Inc. Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. Sanofi-Aventis U.S. LLC, Baxter International Inc., West-Ward Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Abbott Laboratories, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Medtronic plc, Johnson & Johnson, and others. |
| Customization Scope | Free customization report with the procurement of the report, Modifications to the regional and segment scope. Particular Geographic competitive landscape. |
| Pricing and Available Payment Methods | Explore pricing alternatives that are customized to your particular study requirements. |
This study employed a multi-step, mixed-method research approach that integrates:
This approach ensures a balanced and validated understanding of both macro- and micro-level market factors influencing the market.
Secondary research for this study involved the collection, review, and analysis of publicly available and paid data sources to build the initial fact base, understand historical market behaviour, identify data gaps, and refine the hypotheses for primary research.
Secondary data for the market study was gathered from multiple credible sources, including:
These sources were used to compile historical data, market volumes/prices, industry trends, technological developments, and competitive insights.
Primary research was conducted to validate secondary data, understand real-time market dynamics, capture price points and adoption trends, and verify the assumptions used in the market modelling.
Primary interviews for this study involved:
Interviews were conducted via:
Primary insights were incorporated into demand modelling, pricing analysis, technology evaluation, and market share estimation.
All collected data were processed and normalized to ensure consistency and comparability across regions and time frames.
The data validation process included:
This ensured that the dataset used for modelling was clean, robust, and reliable.
The bottom-up approach involved aggregating segment-level data, such as:
This method was primarily used when detailed micro-level market data were available.
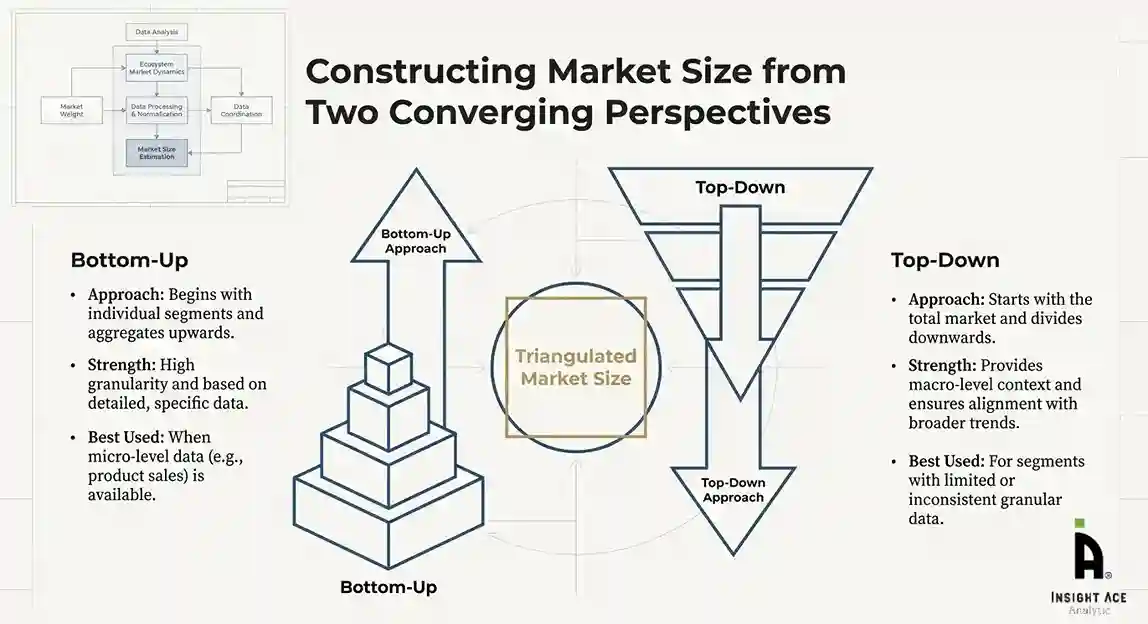
The top-down approach used macro-level indicators:
This approach was used for segments where granular data were limited or inconsistent.
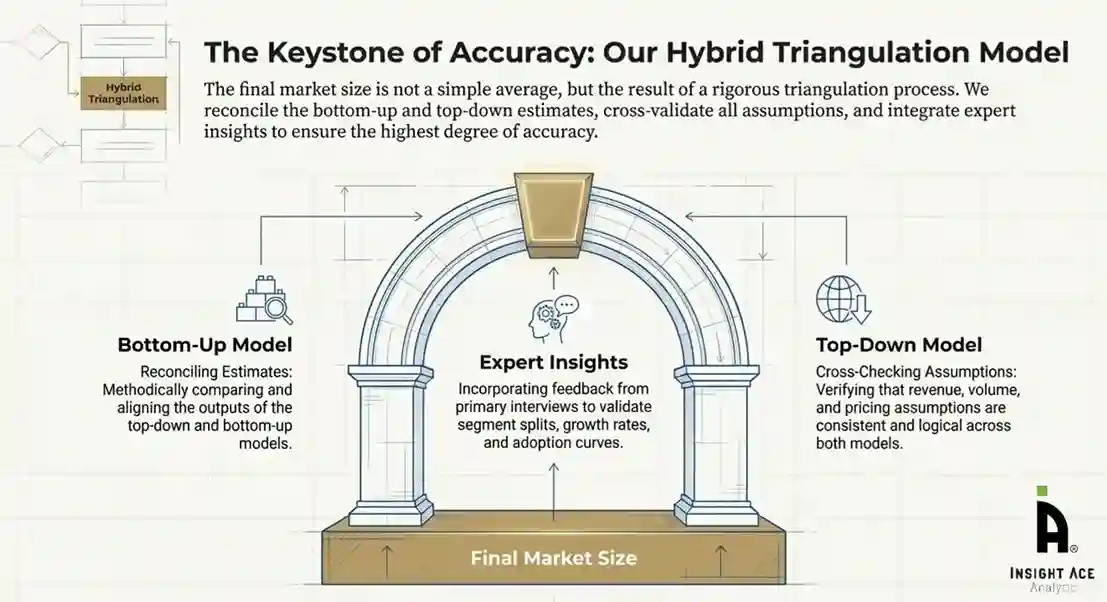
To ensure accuracy, a triangulated hybrid model was used. This included:
This multi-angle validation yielded the final market size.
Market forecasts were developed using a combination of time-series modelling, adoption curve analysis, and driver-based forecasting tools.
Given inherent uncertainties, three scenarios were constructed:
Sensitivity testing was conducted on key variables, including pricing, demand elasticity, and regional adoption.